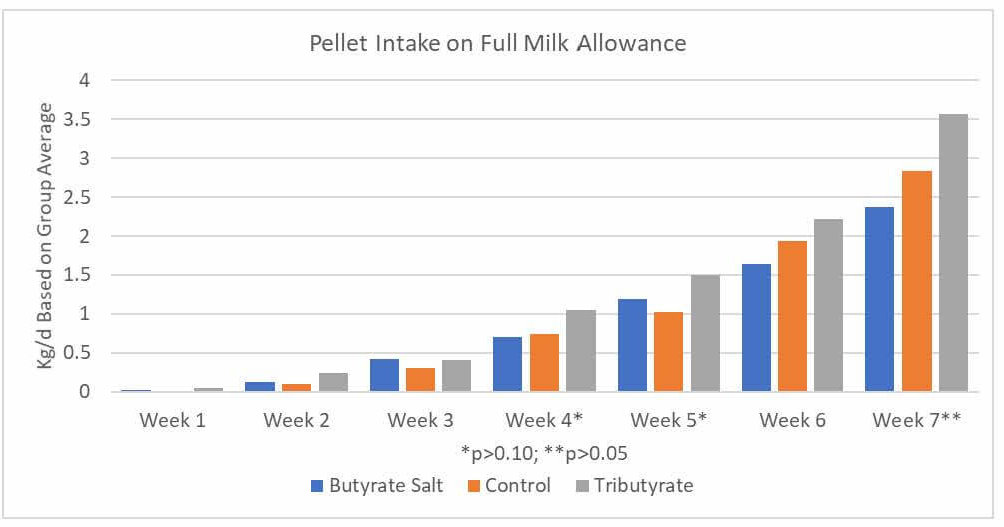
Background
As a major energy source, fat is an important element to consider in a calf milk replacer. Type of fat and the selection of emulsifiers impact the digestibility of triglycerides (fats), and thus subsequent metabolism and incorporation into body tissues. Fat, however, has other nutritional effects beyond a source of energy. Essential fatty acids, such as omega-3, are critical to support neurological functions and modulation of inflammatory response. Moreover, medium chain fatty acids, such as those found in coconut oil and butterfat, are not only easy to digest by a young calf, but also have positive health benefits due to antimicrobial/antiviral properties. Butterfat offers a unique fatty acid, namely butyric acid. As extensively studied in animal and human research, butyric acid is an interesting short chain fatty acid. The use of butyrate products in humans has shown to be effective in improving intestinal health of individuals compromised with health conditions such as Crohn’s disease.